OSPF in single area network is a scalable and reliable protocol, allowing for the efficient management of routing information in large and complex networks.
Different between OSPF in a single area and OSPF In Multiple Areas
OSPF can be implemented in a single area or multiple areas, and there are some key differences between the two:
- Area structure: In a single area OSPF network, all routers are in the same area, and they share the same routing information. In contrast, in a multi-area OSPF network, routers are organized into different areas based on their geographic location, and each area has its own topology database and routing table.
- Scalability: Single area OSPF networks can become congested and slow down as the network grows larger and more complex, whereas multi-area OSPF networks can be scaled more easily by partitioning the network into smaller areas.
- Control: Multi-area OSPF networks provide greater control over the distribution of routing information, allowing administrators to better manage the flow of traffic between different areas.
- Efficiency: Single area OSPF networks are more efficient at distributing routing information within a small, simple network, while multi-area OSPF networks are more efficient at handling a larger, more complex network with many different types of traffic.
about the Notes:-
The book is a quick and comprehensive summary of OSPF In Single Area. consisting of 27 pages, in a simple style.






Notes Content: –
- OSPF C/C‘s
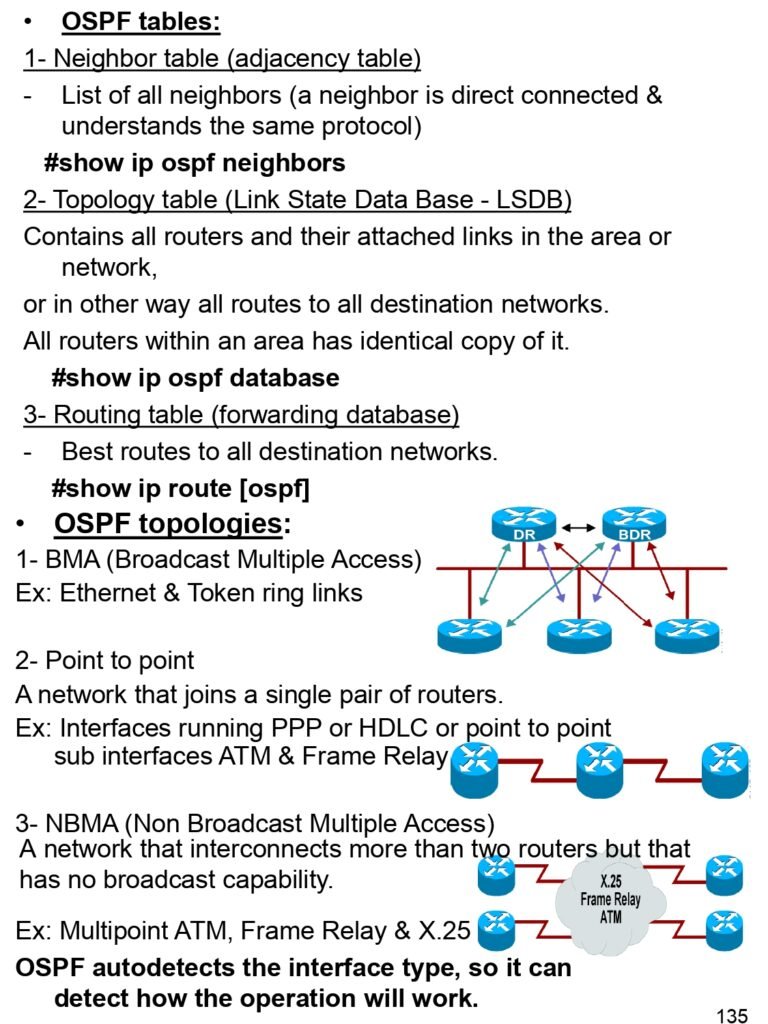
- OSPF tables
- Neighbor table (adjacency table)
- Topology table (Link State Data Base – LSDB)
- Routing table (forwarding database)
- OSPF topologies
- BMA (Broadcast Multiple Access)
- Point to point
- NBMA (Non Broadcast Multiple Access)
- OSPF packet types
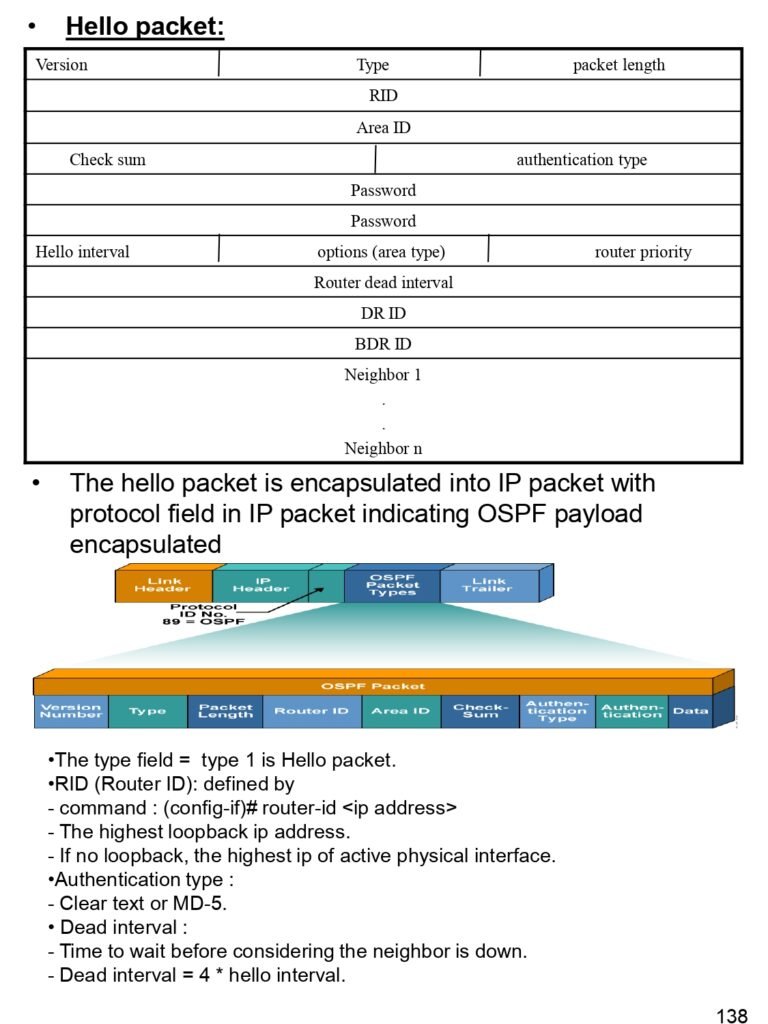
- Hello packet
- DDP (DBD)
- LSR
- LSU
- LSACK
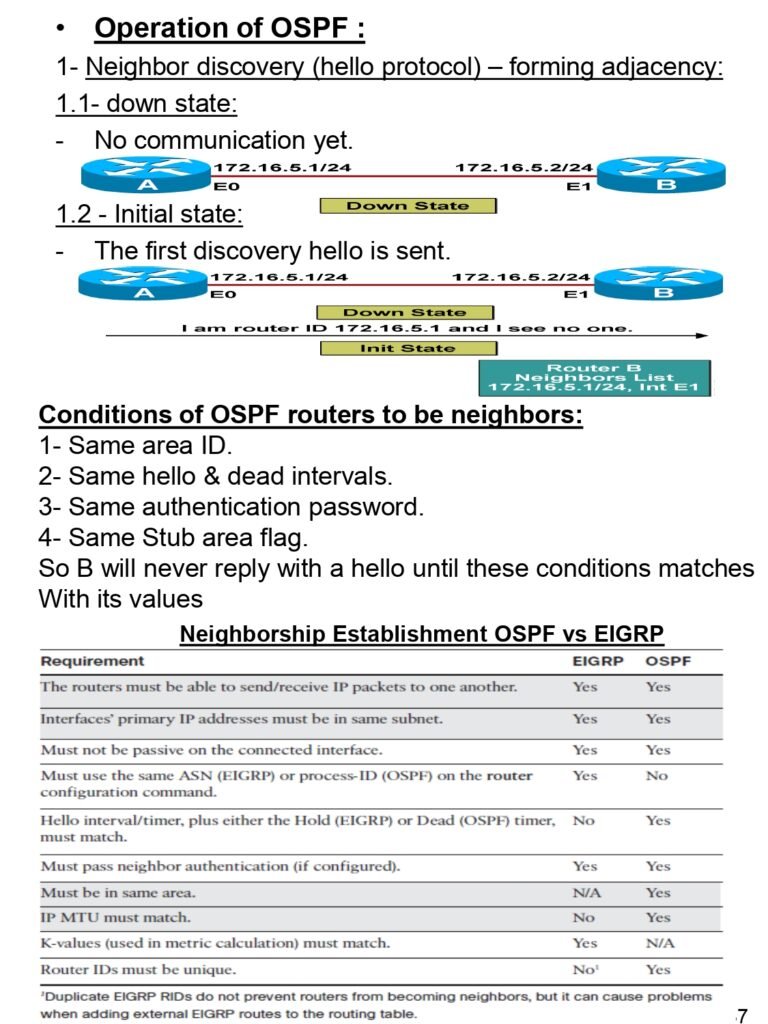
- Operation of OSPF
- Neighbor discovery (hello protocol) – forming adjacency
- down state
- Initial state
- Two way state
- Conditions of OSPF routers to be neighbors
- Neighborship Establishment OSPF vs EIGRP
- Election of DR & BDR (if not exist) – in case of BMA and NBMA
- Routes discovery
- Exstart state
- Exchange state
- Loading state
- Full State
- LSA Sequence Numbering
- LSA Operation
- Creation of Adjacencies
- Choosing routes
- Operation of OSPF in point to point
- At convergence
- At change
- Convergence stability
- SPF delay time
- SPF hold time
- OSPF configuration
- OSPF Router Authentication
- OSPF Troubleshooting
- OSPF operation in NBMA networks
- Configuration for NBMA networks
- Routers in an NBMA mode
- Routers in Multipoint mode
- Routers using point-to-point subinterfaces
Prepared By: –
Eng Ahmed Nabil
Notes Format: –
To Download PDF: –
For MPLS PDF handwriting From here
For BGP PDF handwriting from here








