When OSPF in multiple areas is implemented, the network is divided into different areas based on geographical location or network size. Each area has a unique area ID, and the routers in the area maintain a link state database (LSDB) containing information about the network topology.
Different between OSPF in a single area and OSPF In Multiple Areas
OSPF can be implemented in a single area or multiple areas, and there are some key differences between the two:
- Area structure: In a single area OSPF network, all routers are in the same area, and they share the same routing information. In contrast, in a multi-area OSPF network, routers are organized into different areas based on their geographic location, and each area has its own topology database and routing table.
- Scalability: Single area OSPF networks can become congested and slow down as the network grows larger and more complex, whereas multi-area OSPF networks can be scaled more easily by partitioning the network into smaller areas.
- Control: Multi-area OSPF networks provide greater control over the distribution of routing information, allowing administrators to better manage the flow of traffic between different areas.
- Efficiency: Single area OSPF networks are more efficient at distributing routing information within a small, simple network, while multi-area OSPF networks are more efficient at handling a larger, more complex network with many different types of traffic.
about the Notes:-
The book is a quick and comprehensive summary of OSPF In Multiple Areas. consisting of 30 pages, in a simple style.

Notes Content: –
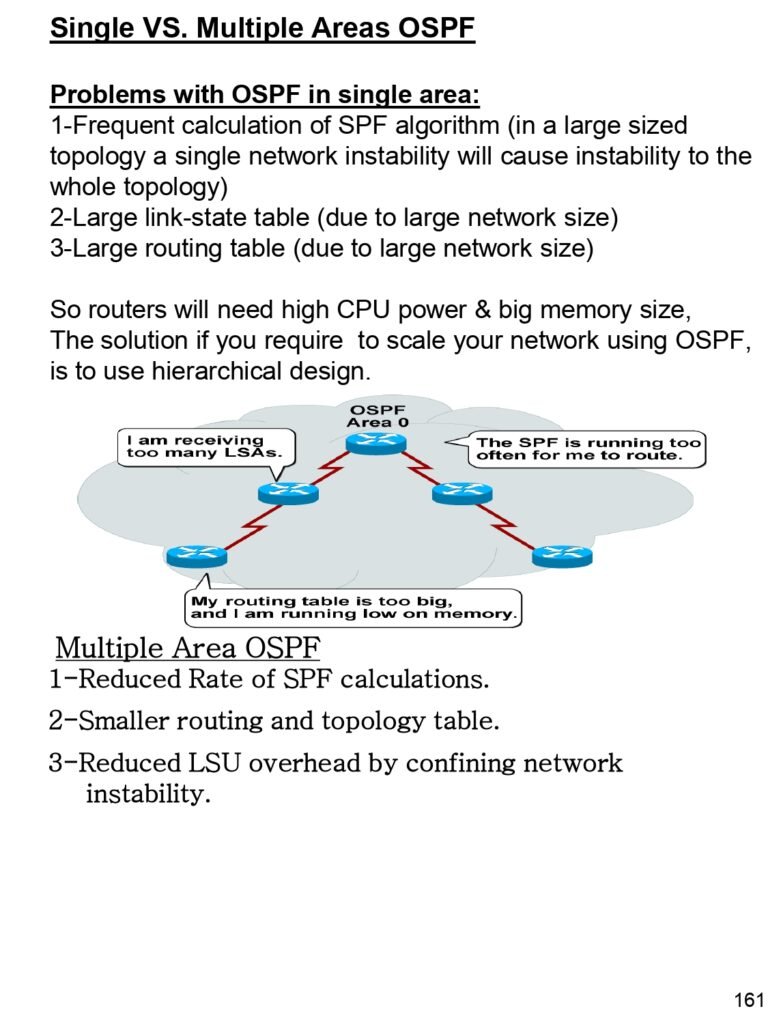
- Problems with OSPF in single area
- Multiple Area OSPF
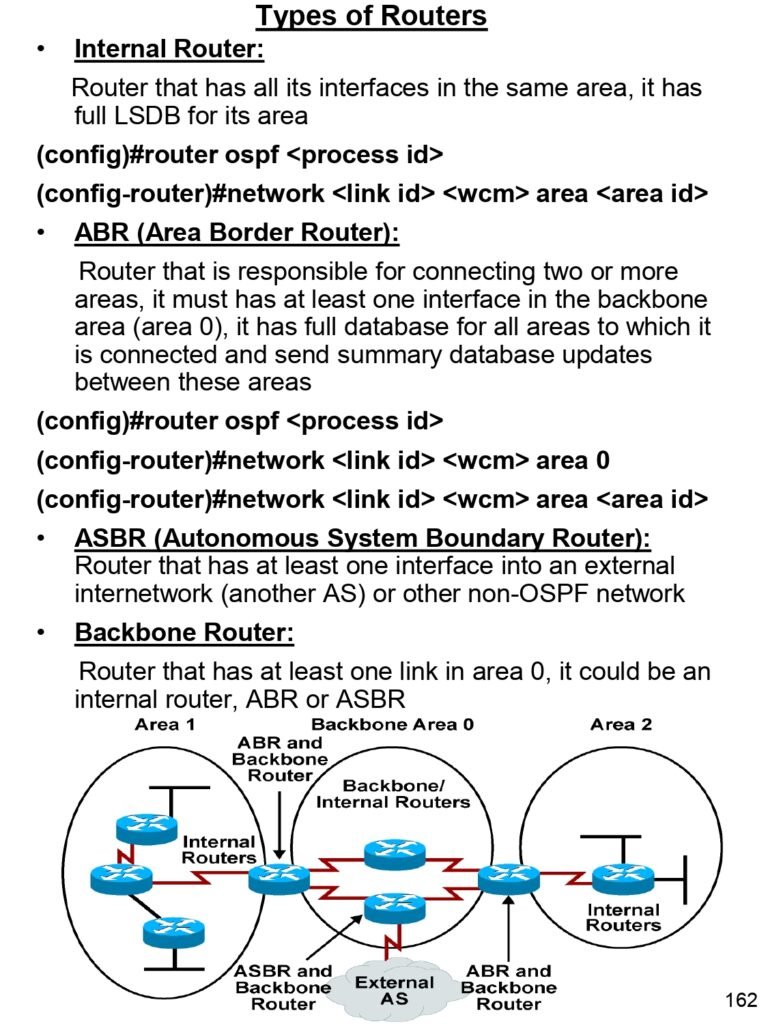
- Types of Routers
- Internal Router
- ABR (Area Border Router)
- ASBR (Autonomous System Boundary Router)
- Backbone Router
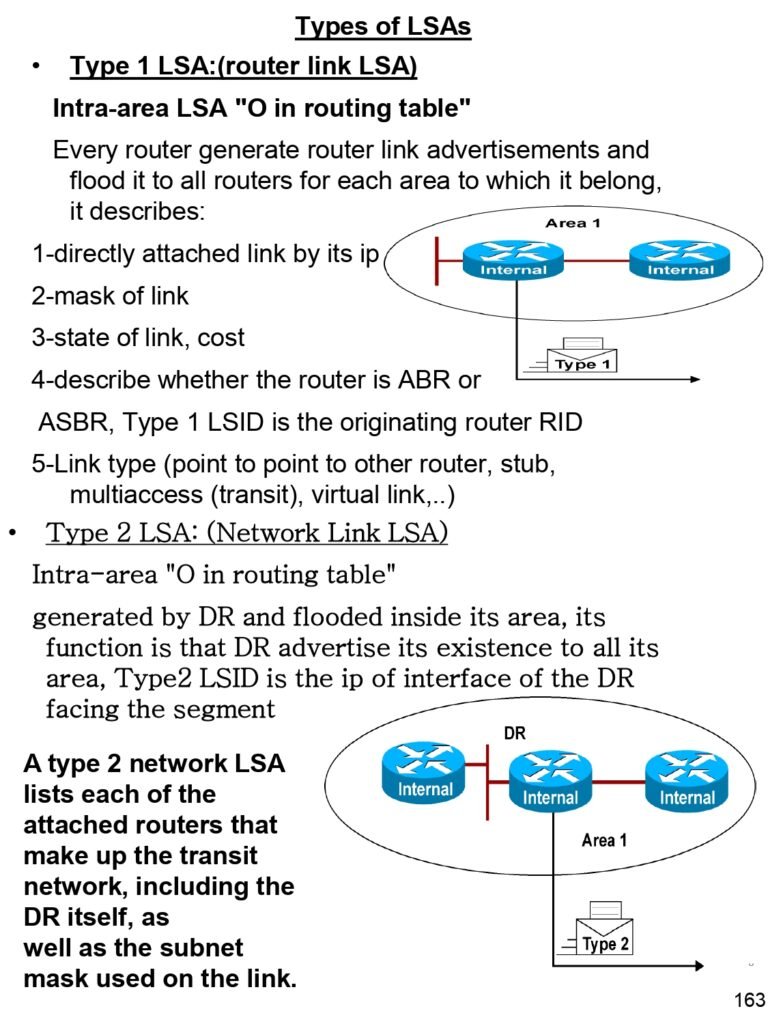
- Types of LSAs
- Type 1 LSA:(router link LSA)
- Type 2 LSA: (Network Link LSA)
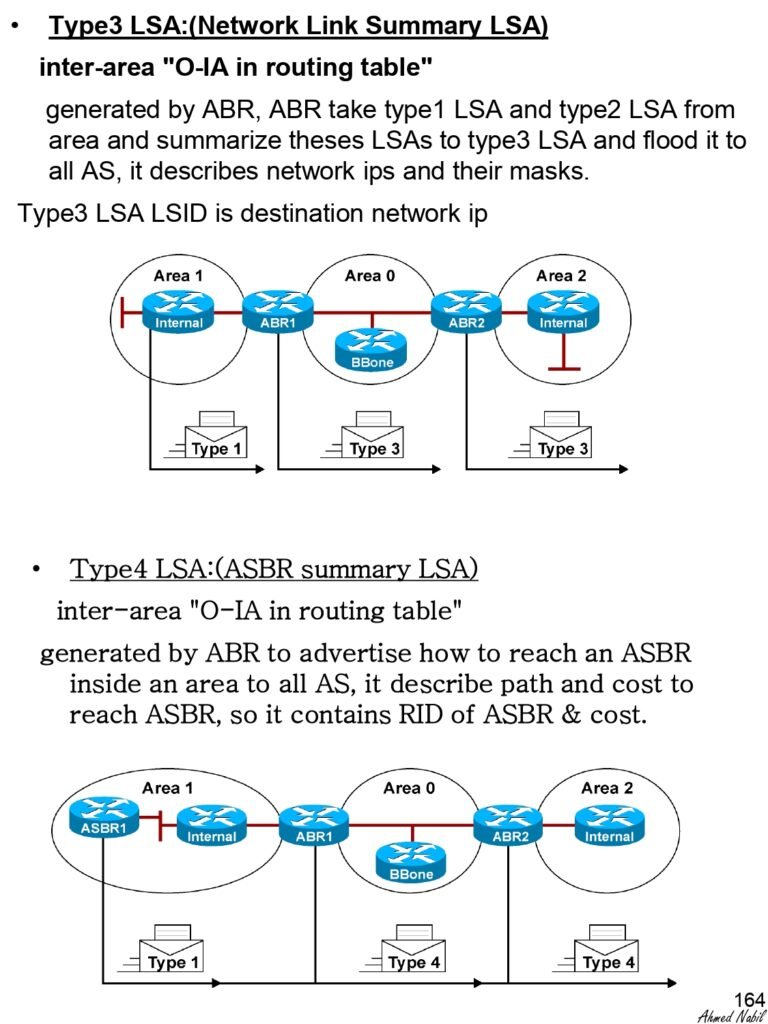
- Type 3 LSA:(Network Link Summary LSA)
- Type 4 LSA:(ASBR summary LSA)
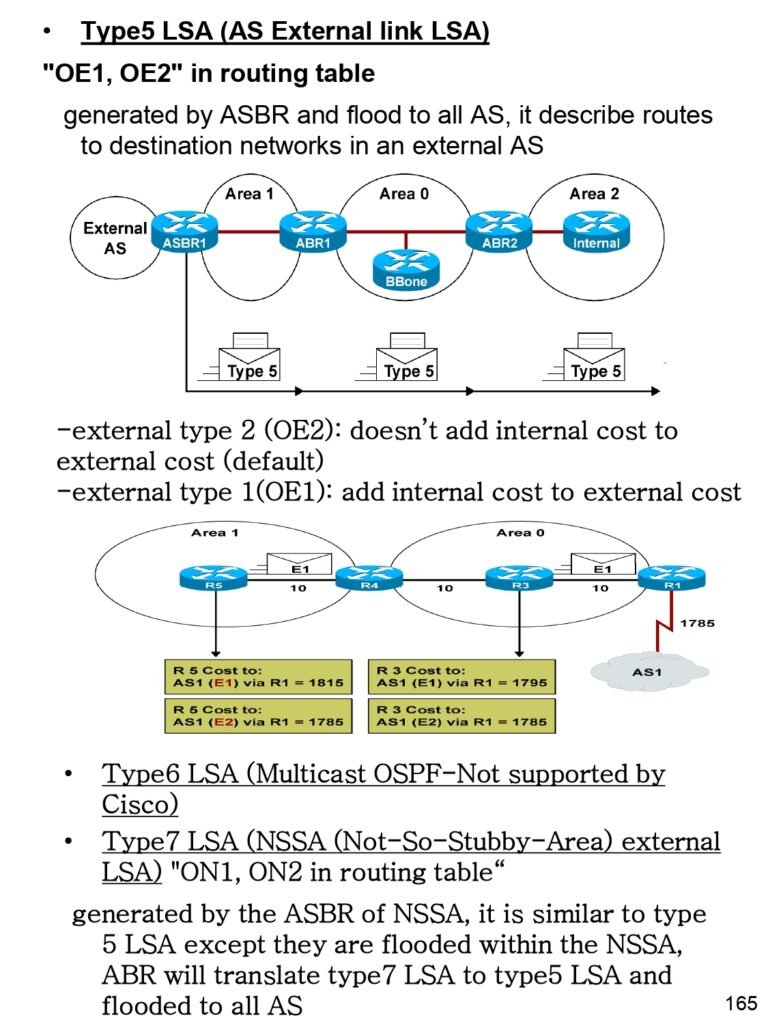
- Type 5 LSA (AS External link LSA)
- Type 6 LSA (Multicast OSPF-Not supported by Cisco)
- Type7 LSA (NSSA (Not-So-Stubby-Area) external LSA
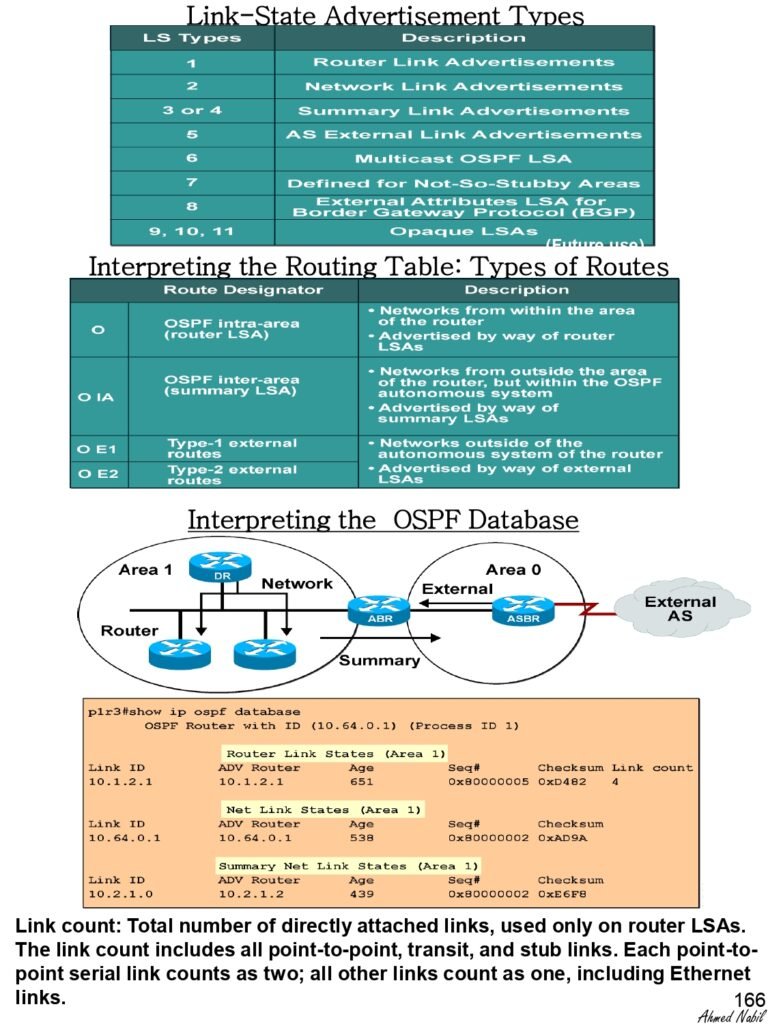
- Link-State Advertisement Types
- Interpreting the Routing Table: Types of Routes
- Interpreting the OSPF Database
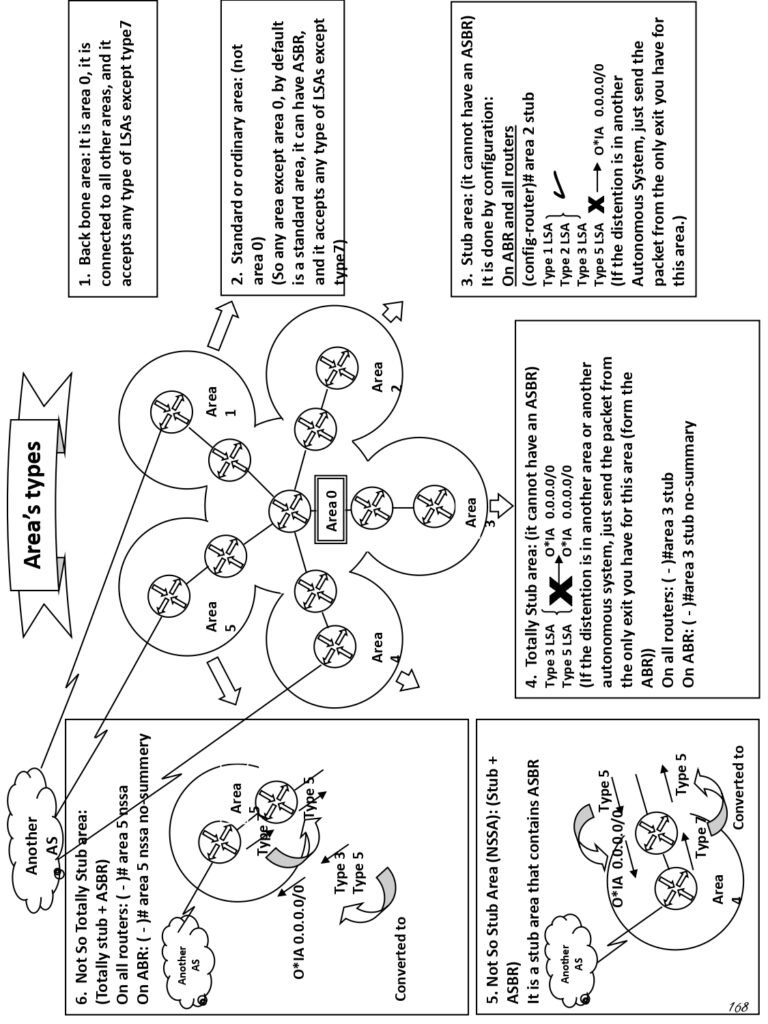
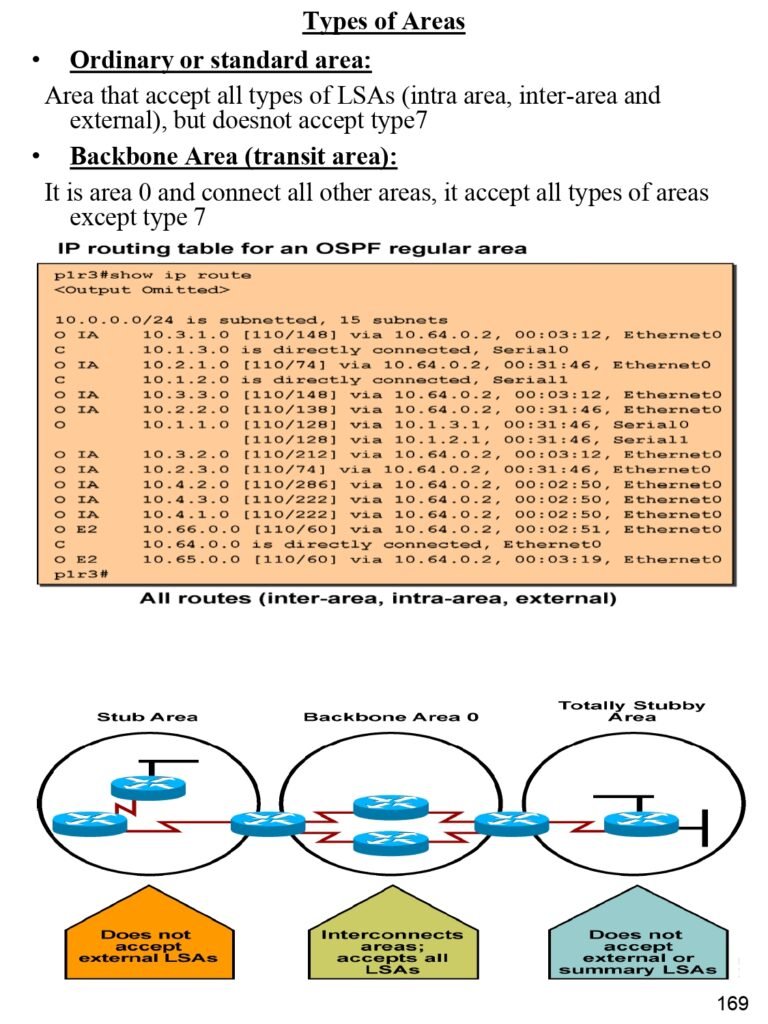
- Types of Areas
- Ordinary or standard area
- Backbone Area (transit area)
- Stub area
- Totally Stub area
- NSSA (Not-So-Stubby-Area)
- Configuring summarization
- OSPF Virtual links
- Verification and troubleshooting
- Design considerations
- How OSPF for IPv6 Works
- OSPFv3—Hierarchical Structure
- OSPFv3—messages
- Enhanced Routing Protocol Support Differences from OSPFv2
- OSPFv3 vs OSPF v2
- LSA Types for IPv6
- OSPFv3 LSA features
- OSPFv3 Configuration
Prepared By: –
Eng Ahmed Nabil
Notes Format: –
To Download PDF: –
For MPLS PDF handwriting From here
For BGP PDF handwriting from here








