STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) Overvew
STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) is a protocol used in network bridges and switches to prevent loops in a network topology. It works by creating a tree-like structure of network paths, with a single designated root bridge at the top.
STP blocks redundant paths in the network to prevent loops, which can cause broadcast storms and network congestion. When a link failure occurs, STP automatically recalculates the network topology and selects a new path.
STP Notes PDF
Small and perfect Notes Discuss Switch Port Aggregation with EtherChannel, consisting of 23 pages, in a simple style.





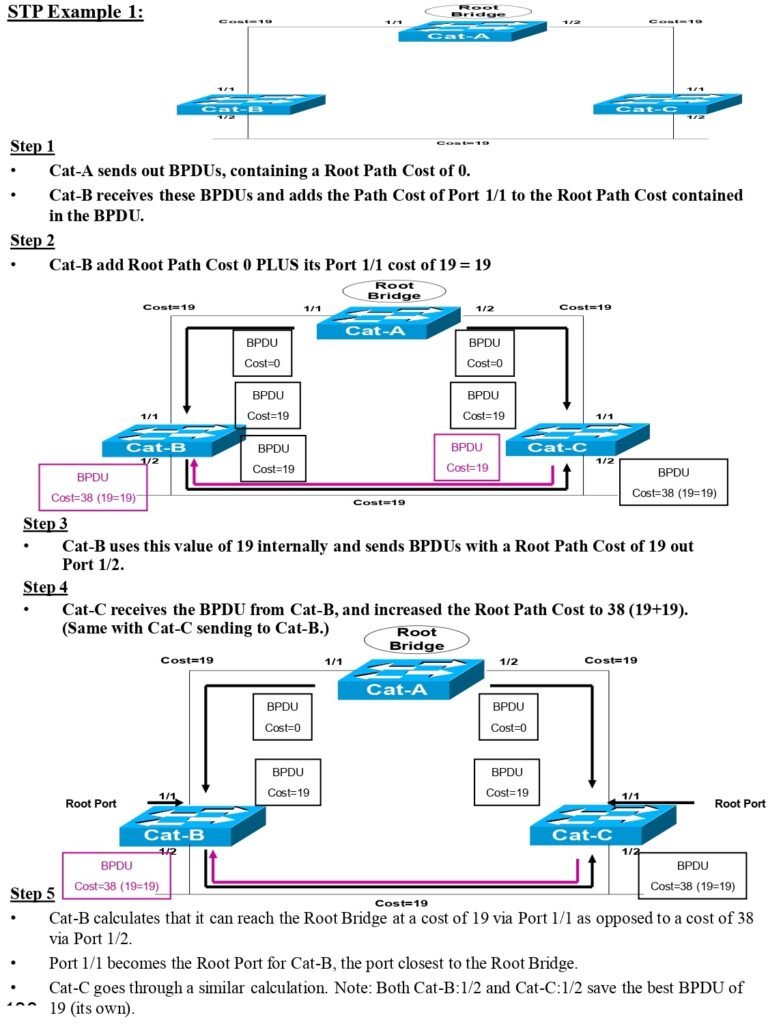
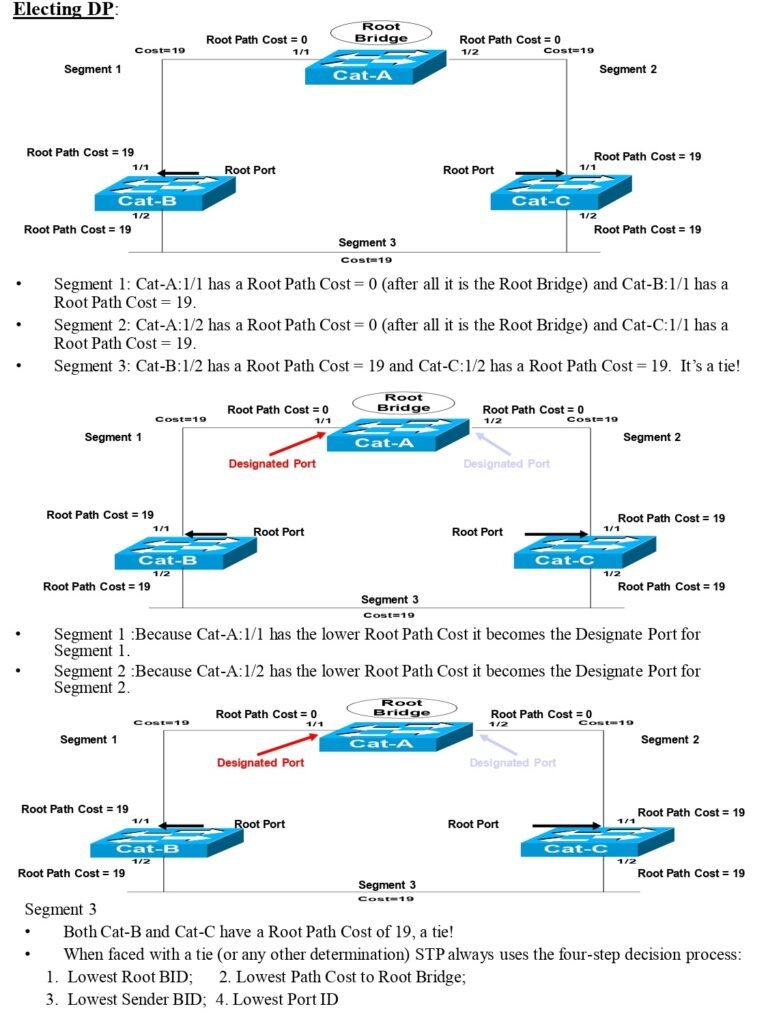
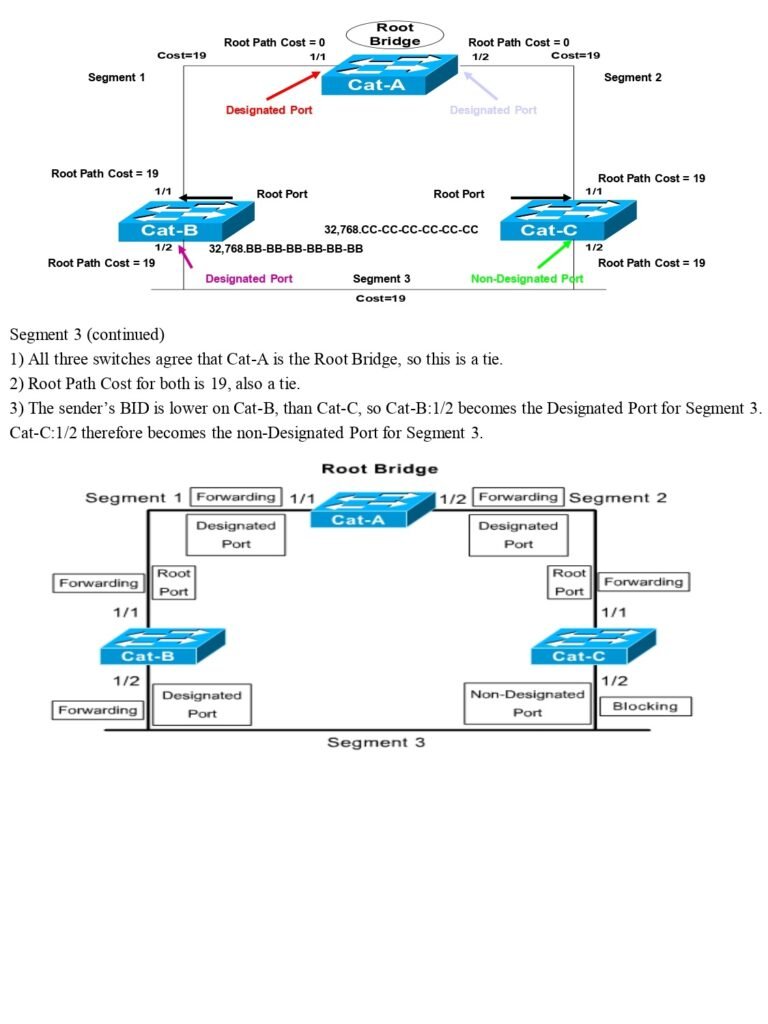
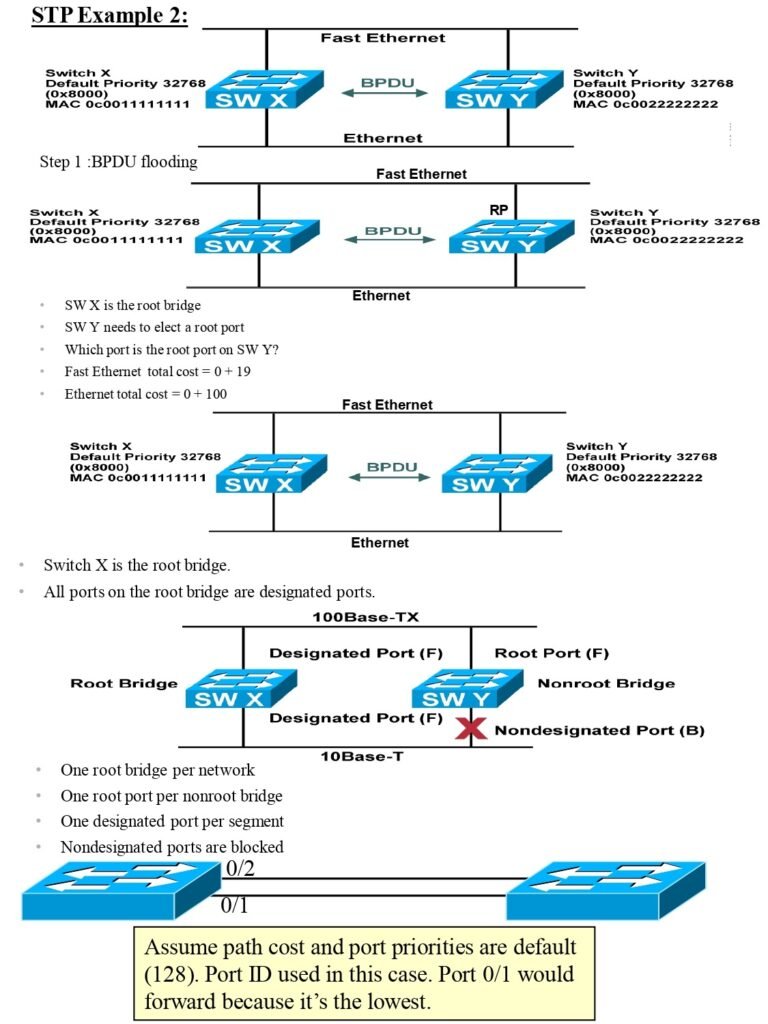
STP Notes Content
- STP (Spanning Tree Protocol)
- STP Overview
- Traditional STP (802.1d) operation
- BPDU (Bridged Protocol Data Unit) flooding
- Electing Root Bridge
- Elect Root Port (RP)
- Elect Designated Port (DP)
- Elect Blocked Port (BP)
- Summarizing the STP process
- STP Examples
- STP Port States
- STP Topology Changes
- STP Enhancements
- Optimizing Spanning Tree Protocol
- Campus Network with an Inefficient Root Bridge Election
- Campus Network with STP Converged
- 802.1D 16-bit Bridge Priority Field Using the Extended System ID
- STP considerations & Enhancements
- Enhancing STP convergence
- Spanning Tree debug Commands
- Protecting the Spanning Tree Protocol Topology
- Protecting Against Unexpected BPDUs
- Root Guard
- BPDU Guard
- Protecting Against Sudden Loss of BPDUs
- BPDU skew detection
- Loop Guard
- UniDirectional Link detection (UDLD)
- EXAMPLE SWITCHED TOPOLOGY
- Using Storm Control
Prepared By: –
Eng Ahmed Nabil
Notes Format: –
To Download PDF: –
For other Network Notes PDF From here
